
Carbonic acid in the water
Carbonic acid
Sum formula:
H
2
CO
3
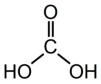
Structural formula:
Diprotic acid
2 dissociation stages
2 pK values
Formation of carbonic acid
Carbonic acid is formed by the chemical reaction of carbon dioxide with water. But only about 0.2% of the carbon dioxide dissolved in water is converted to carbonic acid. (w) = dissolved in water in gaseous formDissociation of carbonic acid to hydrogen carbonate
Carbonic acid as a diprotic acid dissociates in a first step to the hydrogen carbonate ion: pK 1 * (10°C) = 6.5Dissociation of hydrogen carbonate to carbonate
In a second step the hydrogen carbonate ion (as an acid) dissociates to the carbonate ion: pK 2 *(10°C) = 10.5 (*If the pH of the water is equal to the pK of the acid, the acid is 50% dissociated. Values apply to the simplified carbonic acid system).The carbonic acid forms
The following compounds are called carbonic acid forms:
CO
2(w)
Carbon dioxide
H
2
CO
3
Carbonic acid
HCO
3
-
Hydrogen carbonate
CO
3
2-
Carbonate
The gaseous carbon dioxide and the hydrogen carbonate ion are often also called "carbonic acid". The carbonic acid forms are in equilibrium with each other in water:
In
an
open
system
,
however,
these
chemical
dissociation
reactions
have
no
effect
on
the
equilibrium
concentration
of
the
gaseously
dissolved
CO
2
as
long
as
re-equilibration
is
possible
in
contact
with
the
air:
If
gaseously
dissolved
CO
2
is
lost
by
chemical


Anker








