Solution of CO
2
in water
The dissolution of gaseous CO
2
in water
The solution of gaseous CO 2 in water is a physical process. It is a gas exchange between the air and the water. CO 2 from the air passes into the water and at the same time CO 2 molecules from the water pass into the air.
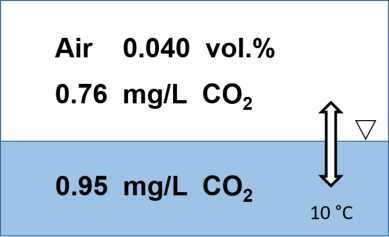
Figure: Distribution of CO2 between air and water
at 0.040% by volume in the atmosphere
An
equilibrium
is
established
between
the
two
processes
when,
per
unit
of
time,
just
as
many
CO
2
molecules
migrate
from
the
air
into
the
water
as
migrate
in
the
opposite
direction
from
the
water
into
the
air.
In
this
way,
the
corresponding
equilibrium
concentrations
are
established
in
the
air
and
in
the
water,
which
correspond
to
the
existing physical conditions (e.g. temperature, pressure).
Solubility
can
be
described
by
the
partition
coefficient
K
or
the
BUNSEN
absorption
coefficient α.
Solubility in water depends on temperature and partial pressure of CO
2
in air.
The
BUNSEN
absorption
coefficient
α
is
about
1.2
for
CO
2
,
which
means
that
at
equilibrium
with
air,
the
concentration
in
water
is
about
1.2
times.
This
in
turn
means
that CO
2
dissolves very well in water (For comparison O
2
: α = 0.38).
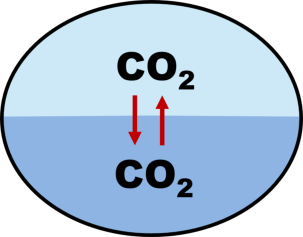
Figure: Gas exchange of CO
2
between air and water
Anker