Anker



Carbon dioxide is an important chemical compound
for the earth and life on earth.
Occurrence of CO
2
:
- in the air
as a gas
- in water - dissolved as a gas - as carbonic acid Hydrogencarbonat-Ion Carbonat-Ion - in rock as carbonate
CO
2
forms the link
between the material world and the living world,
between inorganic and organic, between stone and plant
= Anhydride of carbonic acid
Carbon(IV) oxide
Carbonic acid gas
Carbon dioxide
Dioxomethane
Equivalent designations
Importance of CO2
The Importance of carbon dioxide for the earth and humans
CO
2
• is building block for life through conversion into organic matter • is the main nutrient for plants, both on land and in water • is part of the carbon cycle • influences the climate as a greenhouse gas • is involved in the earth's crust in the form of carbonates as mineral formers • promotes weathering as a water constituent • significantly influences the properties of a water • is often a problem for drinking water quality • often makes water treatment necessary • is the engine for cold water geysers • can cause death at high concentrations in the air
Figure: Occurrence of CO
2
CO
2
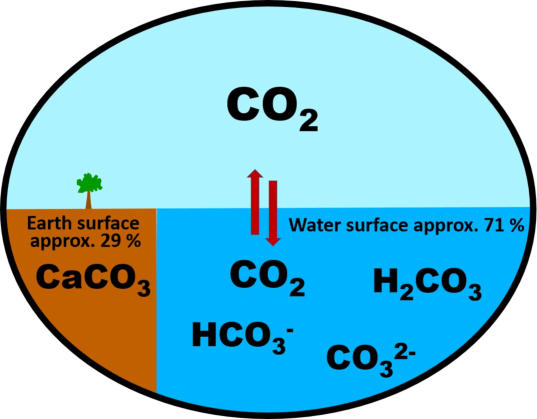

Figure: CO
2
as a link between the inorganic and organic worlds








